Scroll Progress Effect
Scroll down this page to see the progress bar at the top fill up as you scroll. This effect provides visual feedback about reading progress and enhances the user experience.
How It Works
The progress bar uses JavaScript to track the scroll position and calculates what percentage of the page has been scrolled. This value is then applied as a CSS variable that controls the width of the progress bar.
Implementation
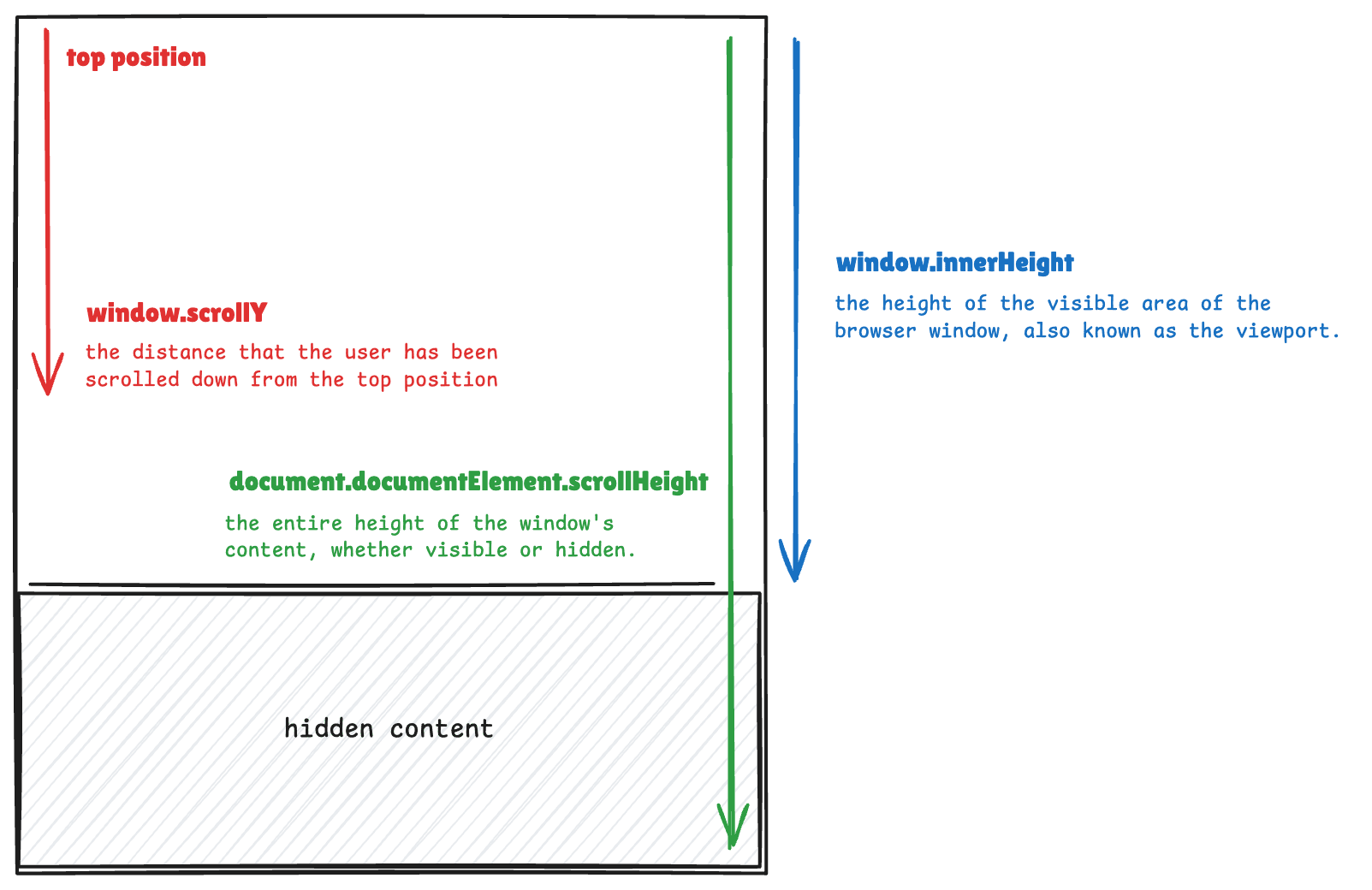
The image above shows us some built-in properties for getting the value of different heights of the window. As a result, in order to calculate the scroll progress, we follow the formula below:
(window.scrollY / (scrollHeight - innerHeight)) * 100
This percentage is then stored in a CSS custom property --scroll-progress, which is used to set the width of the progress bar element in the CSS file:
width: calc(var(--scroll-progress, 0) * 1%);
The document.documentElement.style.setProperty() method in JavaScript is used to set a new value for a CSS property on the documentElement, which represents the html element of an HTML document, which is useful for setting global CSS variables that can be accessed throughout the entire document.
Then, we create a handleScroll function that calculates the scroll progress and updates the CSS variable accordingly. This function is called both on mount and whenever a scroll event occurs. On mount means the very first time the component appears.
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll, { passive: true }); registers a scroll listener so handleScroll runs on scroll.passive: true means the listener will not call preventDefault() and block scrolling.
Finally, we clean up the event listener when the component unmounts to prevent memory leaks.return () => window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);